Protecting Yourself from Phishing: Understanding the Threat and Taking Action
Cybersecurity is an ever-evolving field that requires constant vigilance to stay ahead of the latest threats. One of the most prevalent threats facing individuals and businesses today is phishing. Phishing attacks are designed to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card numbers. In this article, we’ll discuss what phishing is, how it works, and what you can do to protect yourself from it.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack that relies on deception to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information. Typically, phishing attacks are carried out via email, although they can also be carried out through other methods such as social media, phone calls, or text messages.
Phishing emails are designed to look like they are coming from a trusted source such as a bank, an online retailer, or even a friend or colleague. The email will often contain a link to a website that looks like the legitimate website of the organization being impersonated. Once the user enters their information, the attacker can use it to carry out identity theft, financial fraud, or other malicious activities.

How Does Phishing Work?
Phishing attacks work by exploiting the trust that individuals have in the organizations they interact with online. Attackers will often use social engineering tactics to create a sense of urgency or fear in the victim, encouraging them to take immediate action.
For example, an attacker may send an email that appears to be from a bank, claiming that the user’s account has been compromised and that they need to log in immediately to prevent further damage. The email may contain a link to a fake website that looks like the bank’s legitimate website. Once the user enters their login information, the attacker can use it to access the user’s bank account and carry out fraudulent transactions.
Phishing attacks can also be carried out through spear phishing, which targets specific individuals rather than a broad group of users. This type of attack is often more sophisticated and harder to detect, as the attacker has done research on the victim and uses that information to craft a convincing message.
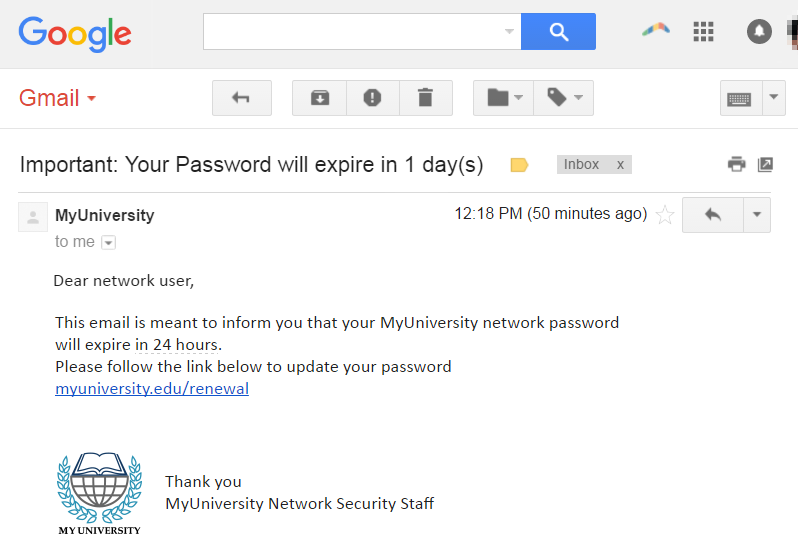
How to Protect Yourself from Phishing
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to protect yourself from phishing attacks:
- Be cautious of emails and messages from unknown senders. If you receive an email that seems suspicious, don’t click on any links or download any attachments until you’ve verified that it’s legitimate.
- Look for signs of phishing in emails. These may include misspelled words, poor grammar, or unusual requests for personal information.
- Verify the sender of an email before clicking on any links. If an email appears to be from a trusted source such as your bank, verify that it’s legitimate by contacting the organization directly.
- Install anti-phishing software on your computer or mobile device. This can help to identify and block phishing attempts before they can do any harm.
- Keep your software and operating system up to date. Phishing attacks often rely on exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated software, so keeping your devices up to date can help to prevent these attacks.

Conclusion
Phishing is a serious threat that can result in identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities. However, by taking steps to protect yourself, you can reduce your risk of falling victim to these attacks. Be cautious of emails from unknown senders, look for signs of phishing, verify the sender of an email before clicking on any links, install anti-phishing software, and keep your software and operating system up to date. With these measures in place, you can stay safe and secure online.
Read More About it here:
- https://www.comptia.org/content/articles/what-is-phishing
- https://consumer.ftc.gov/articles/how-recognize-and-avoid-phishing-scams
- https://www.cnbc.com/2023/01/07/phishing-attacks-are-increasing-and-getting-more-sophisticated.html
